[section]
[section-item]
[row]
[column 12]
[/column]
[/row]
[/section-item]
[/section]
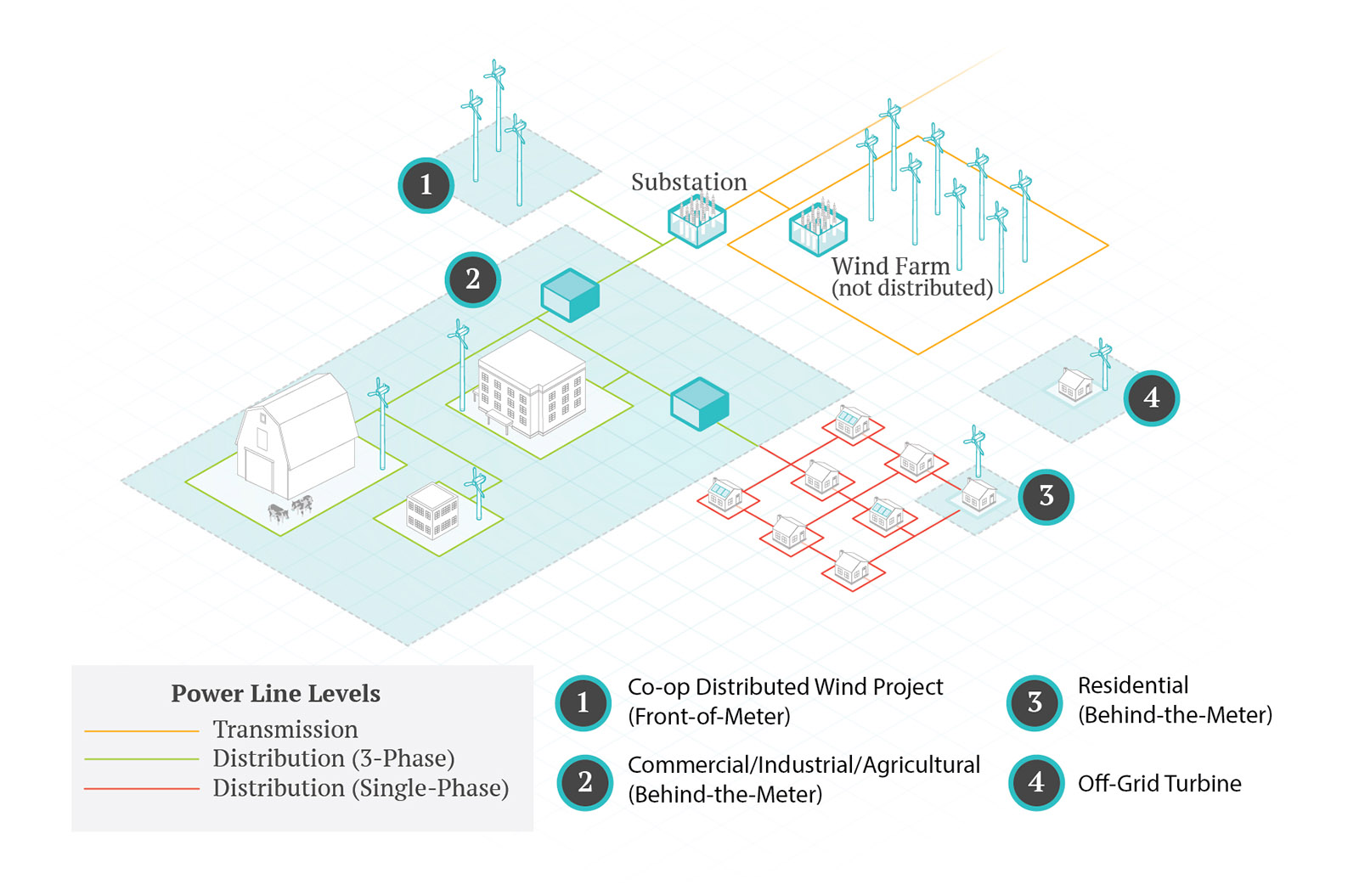
Front-of-Meter
Front of meter projects are projects not connected directly to a metered load and can benefit specific or multiple members. When interconnection policies permit, these projects can be located in favorable wind resource locations and be virtually net metered to a larger load, such as a campus. Otherwise, these sorts of projects can include projects that contribute to a utility’s power supply and might also be cited to provide additional system benefits such as peak reduction. These types of projects can also be part of an isolated utility system, such as many projects in Alaska.
Behind-the-Meter
Residential
A common use for smaller wind turbines is to produce energy for homes and small farms for on-site use.
Commercial/Industrial/Agricultural
Commercial projects can include 3-phase projects serving small businesses, K-12 schools and agricultural processing plants. Industrial projects are ones that are connected at the highest service tier and can include ethanol plants, large (rural) food processing plants, factories and larger campuses.
Off-Grid
Typical
off-grid uses of wind turbines include power for sailboats, remote cabins and
homes, galvanic protection for pipelines, power for remote cellular and radio
sites, and stock water pumping, among other uses.
